
Intelligent Systems Research Group
KARE
AI-supported assistance for hybrid interaction for home care
Team:
Prof. Dr. Astrid Laubenheimer
Prof. Dr. Matthias Wölfel
Samuel Zeitvogel M.Sc.
Christian Felix Purps M.Sc.
Funding: BMBF
Duration: 2022 - 2025
Overview
Elderly people with care needs and their relatives are usually dependent on voluntary and semi-professional support services. If these can no longer be taken advantage of - for example in the case of a pandemic - this puts a strain on the already often fragile care arrangements. At the same time, limited contacts lead to an increased risk of social isolation and loneliness.
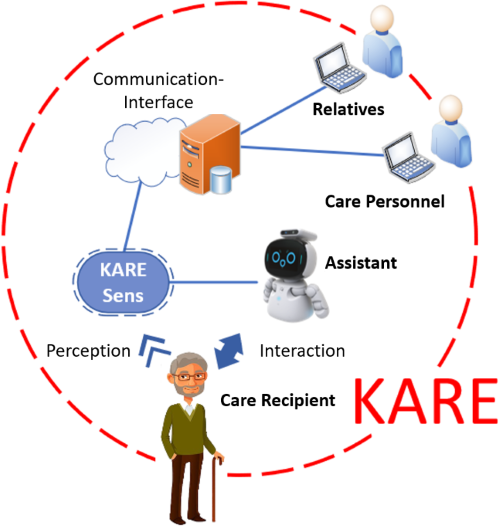
In KARE, a hybrid assistance system was developed that combines ambulatory care provision with a novel AI-based interaction system. A perceptual approach was used to recognize which everyday activities have already been mastered by care recipients and which are still outstanding. If the person in need of care cannot be motivated to perform these actions themselves by being actively addressed by KARE, KARE involves the caregivers in telepresence or on site. For the implementation of the project, the KARE consortium mapped the entire value chain from research to technology to application in care and addresses the entire outpatient service spectrum of ambulatory care, assisted living as well as family caregivers in help-mix arrangements.
KARE supports the quality of life and health of care recipients through a novel, AI-based interaction system, while giving caregivers the freedom to adapt their activities to their own capabilities without limiting care delivery - not only in times of pandemic.
KARE Use Case: Heat Protection
As part of the project, the consortium defined a use case as the central application through which the project results should be implemented. The use case addresses the very current and important topic of heat protection. Due to climate change, we are increasingly confronted with increasingly hotter days. Physical strain increases, particularly during longer periods of heat. In addition, the heat waves are accompanied by a lack of cooling down at night, which prevents restful sleep due to increasingly tropical nights and thus further increases the stress. Heat-related stress, particularly in older people, affects existing risk factors, such as reduced heat regulation in the body. It is therefore important to ensure that you drink enough and regularly in order to prevent the increasing risk of dehydration.
Following the use case, the consortium has built up a database of example videos in the Future Care Lab at the Hochschule Furtwangen. The videos are used for the development and evaluation of the proposed algorithms.
Externer Inhalt
Um diesen Inhalt zu verwenden (Quelle: www.xyz.de), klicken Sie bitte auf Akzeptieren. Wir möchten Sie darauf hinweisen, dass durch die Annahme dieser IFrames Daten an Dritte übertragen oder Cookies gespeichert werden könnten.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie in unserer Datenschutzerklärung.
The KARE Demonstrator
In collaboration the consortium has set up a demonstrator at the HKA with which the functionality of the project results are demonstrated.
Externer Inhalt
Um diesen Inhalt zu verwenden (Quelle: www.xyz.de), klicken Sie bitte auf Akzeptieren. Wir möchten Sie darauf hinweisen, dass durch die Annahme dieser IFrames Daten an Dritte übertragen oder Cookies gespeichert werden könnten.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie in unserer Datenschutzerklärung.
Partners & Funding
Our partners are Hochschule Furtwangen, Inferics GmbH, voice INTER connect GmbH, 3dvisionlabs GmbH, easierLife GmbH, BruderhausDiakonie.
HKA took over the optical and acoustic perception as well as the activity analysis in close cooperation with the technology partners Inferics GmbH, voice INTER connect and 3dvisionlabs. The technology partners extended the optical perception capabilities of PatronuSens multimodally and integrated the sensor platform into KARE-Sens. The easierLife GmbH acted as a system integrator and adapted its cloud infrastructure, and implemented the necessary interfaces, processes and applications. HFU acted as the interface between technical research and the application field of care. The application partner BruderhausDiakonie contributed the necessary practical relevance and works together with the scientific partners HKA and HFU on the methodological planning and implementation of the needs assessment together with elderly clients and the nursing and care staff, the participatory research processes, and the application-related evaluation and is responsible for the organization of the ethical monitoring and the scientific accompanying project.
KARE was funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the funding code 16SV8803.
