
Institute for Intelligent Interaction and Immersive Experience
Projects

Maturity over Manipulation (MuMaSens)
The "MuMaSens" project (Maturity over Manipulation: How to successfully raise awareness of fake news among teenagers and young adults), funded by the MWK Baden-Württemberg and in cooperation with Offenburg University of Applied Sciences, develops innovative, adaptive interaction formats to empower young people in dealing with disinformation. Using participatory approaches, pupils and students are actively involved in the design of formats that enable personalized and lifeworldly learning experiences with the help of modern technologies such as generative AI, virtual reality (VR) and virtual assistants. The aim is to create content that has emotional and personal relevance and thus promotes sustainable media skills. The formats developed are made freely available as Open Educational Resources (OER) and evaluated in close cooperation with schools in the region.

Embodied Conversational Agents in Teaching (ECAsL)
In the project “ECAsL” (Embodied Conversational Agents in Teaching), funded by Stiftung Innovation in der Hochschullehre, IIIX is developing an embodied AI-based assistant designed to support students in their everyday academic life. The digital companion combines natural language interaction with non-verbal communication, helping to support learning processes, foster social skills important for university studies, such as presentation and public speaking, and enhance motivation and enjoyment of university life as a whole. It assists in exam preparation, offers movement breaks and relaxation exercises, and helps structure self-regulated learning. Tested in pilot courses and daily student routines, the companion is accessible via online platforms, on-campus terminals, and mobile devices. The aim is to transform the university into an interactive, barrier-free, and socially supportive learning environment.

Reality Check: Fake or Fact in the Age of Generative AI
The project “Reality Check: Fake or Fact in the Age of Generative AI” raises awareness among young people and educational stakeholders about the risks of AI-generated misinformation. Supported by the Carl Zeiss Foundation and in close cooperation with the ZKM | Center for Art and Media Karlsruhe, interactive workshops with pupils, a public symposium, and digital applications are being implemented. The goal is to enable young people to critically question and use information technologies in a self-determined way. The practical and participatory formats promote sustainable media literacy and can be transferred to a wide range of educational contexts.

Künstliche Intelligenz für Arbeit und Lernen in der Region Karlsruhe (KARL)
Artificial intelligence (AI) support for travel consultations is intended to provide employees with up-to-date topics and information for the consultation. Customers will be shown suitable images in real time when determining their travel requirements in order to get a better idea of the destination.
The goal of the use case led by ADAC Nordbaden is on the one hand to support employees in travel advisory meetings through the use of AI and on the other hand to offer customers a better experience during travel advice. Specifically, the AI is to process current topics and information from ADAC databases ("ADAC data pool") on the basis of the content of the consultation with the customer and make it available to employees in a suitable form. The goal is a noticeable reduction of interruptions in the dialog between employees and customers through shorter research times on the part of the consulting experts at the computer. At the same time, the use of AI is intended to provide visual support for the advice given, with customers seeing suitable images on monitors in real time for the destinations, hotels or activities mentioned.
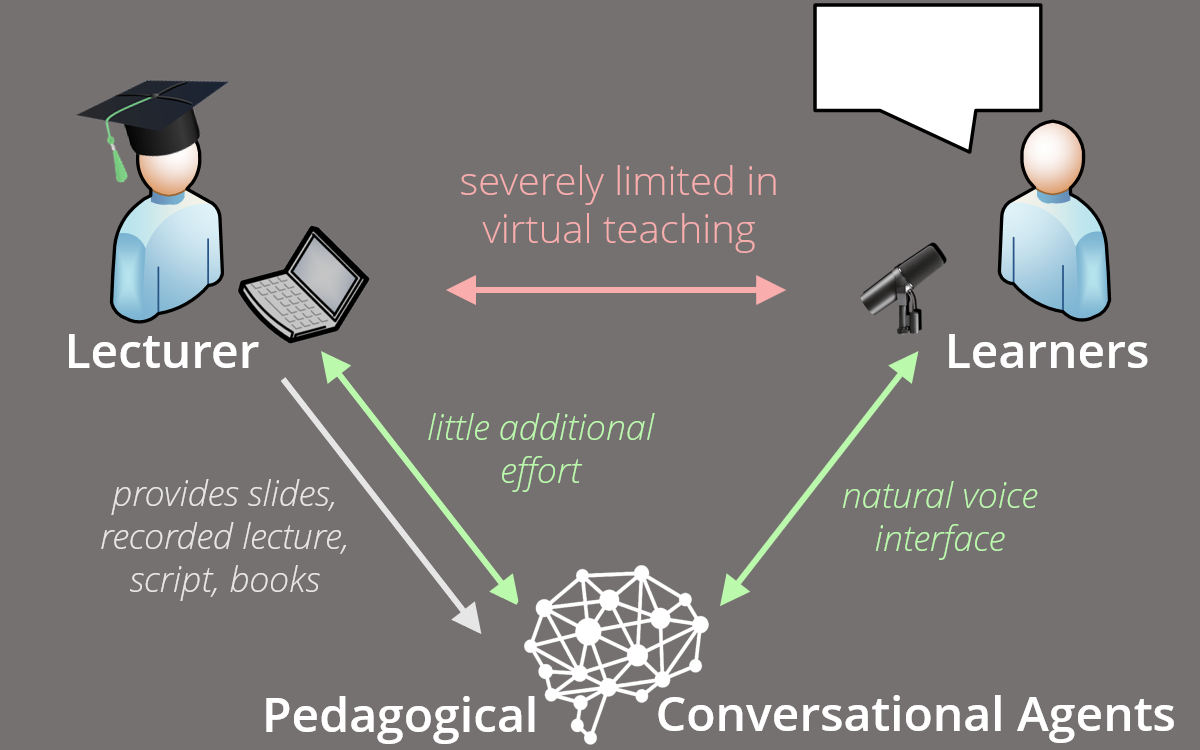
The PEdagogical conversational Tutor (PET)
The PEdagogical conversational Tutor (PET) is a web-based language assistance system that is developed in the bounds of a research project of the "Stiftung für Innovation in der Hochschullehre". The project is a cooperation project between the University of Hohenheim and the Hochschule Karlsruhe and lead by Prof. Dr. Matthias Wölfel. The PET can be used by learners in addition to lectures to review courses and to prepare for exams. Natural language can be used to retrieve lecture content and even check students' knowledge. The system learns lecture content independently based on information provided by lecturers, such as lecture slides and recordings, and can thus be used for any lecture without much effort on the part of the teaching staff. This is made possible by several AI systems (especially Natural Language Processing) working hand in hand. The system is currently in use at Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences and will also be used for several courses at the University of Hohenheim in the coming winter semester.

Doctoral Colleges

Accessibility through AI-based Assistive Technology
The Cooperative Graduate School Accessibility through AI-based Assistive Technology (KATE) is a new cooperative and interdisciplinary graduate school between the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) and the Hochschule Karlsruhe (HKA).
Are you interested in improving the quality of life of persons with special needs by using state of the art artificial intelligence methods to develop assistive technology for these user groups? For example by supporting a user’s independence in mobility and orientation using state-of-the art computer vision and the design of appropriate user interfaces to such technology; or by enabling better accessibility of documents, for example to the graphical elements in books or multimedia documents; or by building robotic tools to assist persons with mobility impairments? Or are you interested in investigating the ethical, social and societal impacts of such technology? Then please take a look at the proposed PhD projects. If you have ideas how to approach some of these topics, please send your application to the doctoral program.

Knowledge Media
How can digital technologies be used effectively and purposefully in school and university teaching? Which didactic approaches should be applied and which technologies are suitable for which subject contents? These questions are the focus of the new cooperative doctoral program "Knowledge Media. Technology, Learning and Application from an Interdisciplinary Perspective", which started its work at the beginning of March at the Karlsruhe University of Education (PHKA), Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences (Die HKA) and Furtwangen University of Applied Sciences (HFU).
Completed Projects

MERLOT
The MERLOT (MarkEtplace foR LifelOng educaTional dataspaces and smart service provisioning) project, funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK), will create specially protected educational data spaces and services within the Gaia-X ecosystem. These ensure that the owners of educational data always retain sovereignty over their data and can make it available to other users or services in an interoperable manner as required. Learners, schools, public institutions, administrations or companies are thus enabled to exchange educational data in a GDPR-compliant manner and to share it in a controlled manner without having to conclude separate individual agreements with each participant.
Our main objective is the study of human-computer interaction models based on Artificial Intelligence, embodied agents and chatbots, in order to create trustful interactions and offer accurate answers to the educational and career orientation scenario.
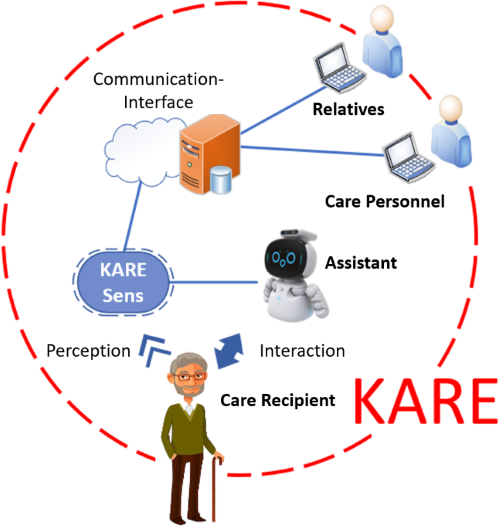
KARE
In KARE, a hybrid assistance system is developed that combines ambulatory care provision with a novel AI-based interaction system. A perceptual approach is used to recognize which everyday activities have already been mastered by care recipients and which are still outstanding. If the person in need of care cannot be motivated to perform these actions themselves by being actively addressed by KARE, KARE involves the caregivers in telepresence or on site. For the implementation of the project, the KARE consortium maps the entire value chain from research to technology to application in care and addresses the entire outpatient service spectrum of ambulatory care, assisted living as well as family caregivers in help-mix arrangements.
KARE supports the quality of life and health of care recipients through a novel, AI-based interaction system, while giving caregivers the freedom to adapt their activities to their own capabilities without limiting care delivery - not only in times of pandemic.
Liveness Detection
The objective of this project is to develop a reliable and secure liveness detection system for online identification purposes, such as opening a bank account or registering a prepaid phone number. The system will use advanced computer vision and machine learning algorithms to analyze a user's facial movements and detect whether the person is real or attempting to deceive the system. Additionally, the project will focus on enhancing image quality for identity card recognition, as low-quality images can lead to errors in identification. This will involve developing image enhancement techniques that can improve image resolution, brightness, contrast, and other parameters to increase the accuracy of identity card recognition.
The project will also incorporate live feedback for hologram detection on identity cards, providing real-time instructions to users on how to improve the quality of the hologram image. For example, if the hologram image is unclear, the system may provide feedback such as "rotate your identity card left" or "put your identity card in a place with better lighting" to help the user capture a high-quality image. Overall, the project aims to create a robust and accurate system for online identification that leverages cutting-edge computer vision and machine learning techniques, while also providing live feedback to users to improve the quality of the identity card images captured.
AR-INSIGHT
AR-INSIGHT is a cooperation project between the Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences and industrial partners, AUNOVIS GmbH (Karlsruhe) and AMAISYS TECHNOLOGIES SLU (Barcelona), working on sensor data fusion for augmented reality (AR) assistance systems in dynamic industrial environments.
The project creates an interactive assistance system featured with head-mounted AR and is made possible by artificial intelligence methods. The aim is to support machinists and other technical personnel in maintenance, control, and monitoring tasks in manufacturing facilities. Relevant key figures and statuses as well as instructions and maintenance manuals are to be superimposed on the machines in order to master the continuously increasing complexity in today's production environment, thus facilitating the implementation of the work process and reducing the burden on the worker.
The accurate recognition of machine or machine movements with regard to dynamics and complexity requires new multidimensional sensor data fusion methods in combination with artificial intelligence techniques that are developed by the Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences.

SHELLS
Augmented and virtual reality expand our possibilities for communication, collaboration and information transfer. In the course of the digital transformation, the confident use of these technologies is a digital competence that is becoming increasingly important.
In the courses focusing on "Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality Technologies", students learn the basics of AR and VR technologies in a practice-oriented manner.
Central components of the course are designing, modeling and developing AR and VR applications as well as teaching, learning and collaborating in immersive environments.

Teilhabe Digital (Digital Participation)
Under the project title Teilhabe Digital (Digital Participation), the Catholic University of Applied Sciences Freiburg, the Furtwangen University of Applied Sciences and the Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences have joined forces with the Caritas Bundesverband Behindertenhilfe und Psychiatrie, the Caritasverband Freiburg-Stadt , the Lebens- und Arbeitsgemeinschaft Lautenbach and the Sankt-Josefshaus Herten to research the use of modern technologies that can increase the social participation opportunities of people with intellectual disabilities.

BMBF-Projekt: Sprachsegmentierung und ihre Anwendungen in Meetings (SAM)
The SAM project has set itself the goal of developing processes and applications that improve communication in virtual meetings as well as their organizational flow in order to increase the efficiency of meetings. This includes the development of cost-effective methods for improving the audio signal in meeting rooms as well as new solutions for segmenting the audio signal. This segmentation is used to assign the audio signal to the corresponding speakers in order to clearly identify who spoke when, where and for how long. Accurate speaker assignment is fundamental for all further steps of speech processing, such as feedback to meeting participants about their speaker participation in the form of Smart Meeting Guidance. Since the listed goals are very difficult or even impossible to achieve on the basis of a single-channel recording, as is often the case in meeting rooms, the aim is to enable multi-channel recordings by interconnecting the microphones of participants' smartphones.

KI-Nachwuchs@FH 2021: Aufbau einer verteilten IT-Infrastruktur für latenzkritische KI-Anwendungen
Building on the expertise available at Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences (HKA) and the strategic orientation in the area of the research focus Intelligent Systems, software architectures, technologies and development methods for latency-critical AI applications are to be researched and taught.
For this purpose, a basic AI-capable IT infrastructure is to be established in the project. This infrastructure shall be applicable for university-wide use in research and for the training of young scientists.
The use of the ILKA IT infrastructure for low-latency AI applications is to be made possible for the three main application areas of robotics in production, intelligent perception and assistance systems, and intelligent IT infrastructures before the end of the project.
With the infrastructure then established and the experience gained from the three pilot projects, an expansion to further application areas and new user groups is to follow after completion of the ILKA project.
Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung (PRISMA)
With the Prisma funding, Prof. Dr. Matthias Wölfel, CZS Endowed Professor for Intuitive and Perceptive User Interfaces, is expanding a toolkit developed in his research group to enable broad application in science and industry. Virtual reality (VR) has become firmly established in recent years and is used in numerous application areas. However, a systematic investigation of applications often fails because the development of test routines in virtual environments is still a major challenge. So far, neither a procedure could be established nor do satisfactory toolkits exist that facilitate access. Professor Wölfel's working group has therefore developed the Virtual Scientific Toolkit. The toolkit is available as open source software and is to be further developed within the framework of Prisma funding.
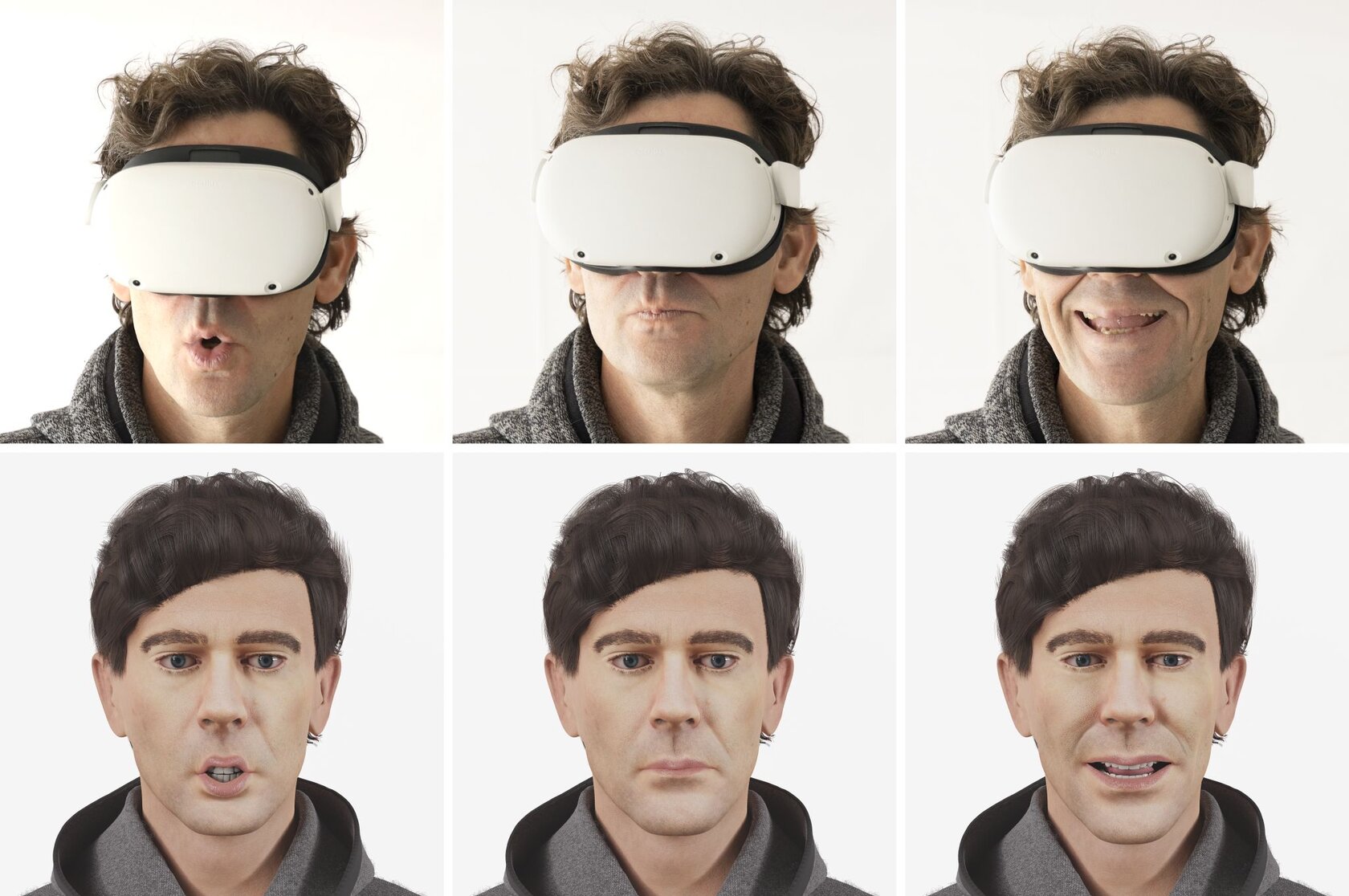

SelfVR Carl-Zeiss-Stiftung
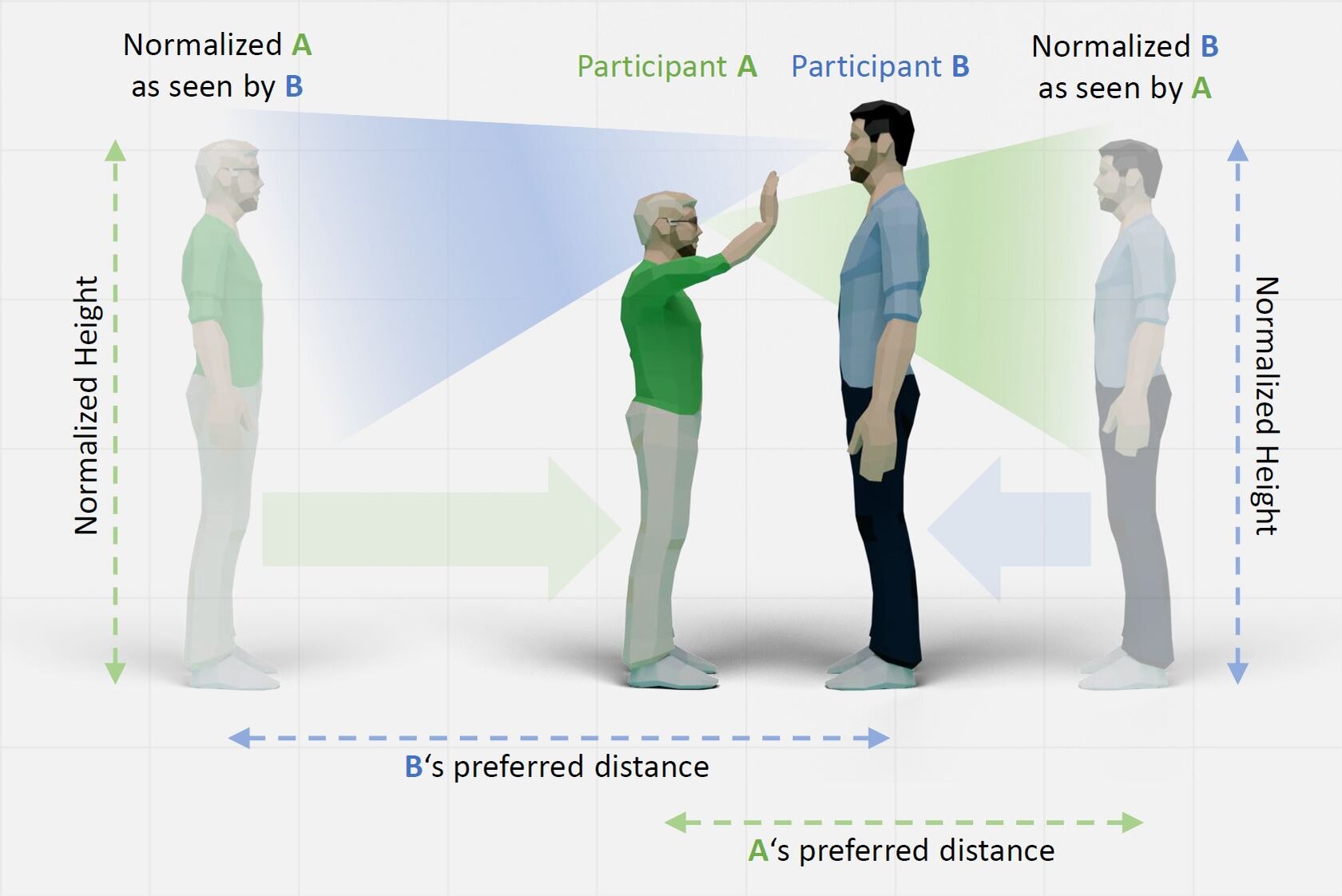
"Social VR" combines telepresence (communication with others but without spatial reference) and VR (high presence and immersion without communication with others) to cleverly combine the respective special features: this enables communication with others with spatial reference and makes the "physical" presence of others tangible. In such environments, a virtual avatar serves as a proxy for the user in the virtual environment. However, the appearance and expressiveness of the virtual avatar as a proxy for the head-mounted display user are still severely limited today, both in terms of visual realization and movement.
It is currently not possible to buy a ready-made system "out of the box", but the existing developments (which are often available as open source solutions to the scientific community) open up a rapid implementation. Only the sensible combination of the individual technologies virtual reality, 3D scanning, auto-rigging, sensor acquisition, pattern recognition and animation make it possible to develop a system that can be used beyond the respective expert circles. It is expected that through the development, further development and use of the overall system, new insights can be gained both from a technological and a social science perspective, which would not be possible or only possible to a reduced extent through the use of individual components.
Read More