HCCI
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition
The research project focuses on the development of a homogeneous charge compression ignition (HCCI) process for a monovalently operated small natural gas CHP unit. Due to the nearly simultaneous auto-ignition of the entire, extremely lean fuel-air mixture in the HCCI process, an approximation to the thermodynamically efficiency-optimal equal-space process is achieved with a parallel reduction of the combustion temperature. Based on the flame-front combustion of the series combustion process, "controlled auto-ignition" is initially realized by means of an intake temperature increase and greatly increased compression, and the operating behavior of the engine in the HCCI process is determined. The focus of the investigations is on the relationship between NOx emissions and efficiency. Due to the extremely high pressure gradients in HCCI combustion and the strongly time-dependent auto-ignition, special attention will also be paid to the achievable load and speed range. Based on the results obtained, measures are being developed to mitigate the trade-off between NOx emissions and efficiency and to extend the operating limits (see also HSACI).
![[Translate to English:] Modellhafter Vergleich von HCCI- (links) und Flammenfrontverbrennung (rechts), nach Onishi et al. (1979)](/fileadmin/_processed_/c/f/csm_HKA_WE-IKKU_Imagefoto_GenLab_HCCI_01_d634651c4e.png)
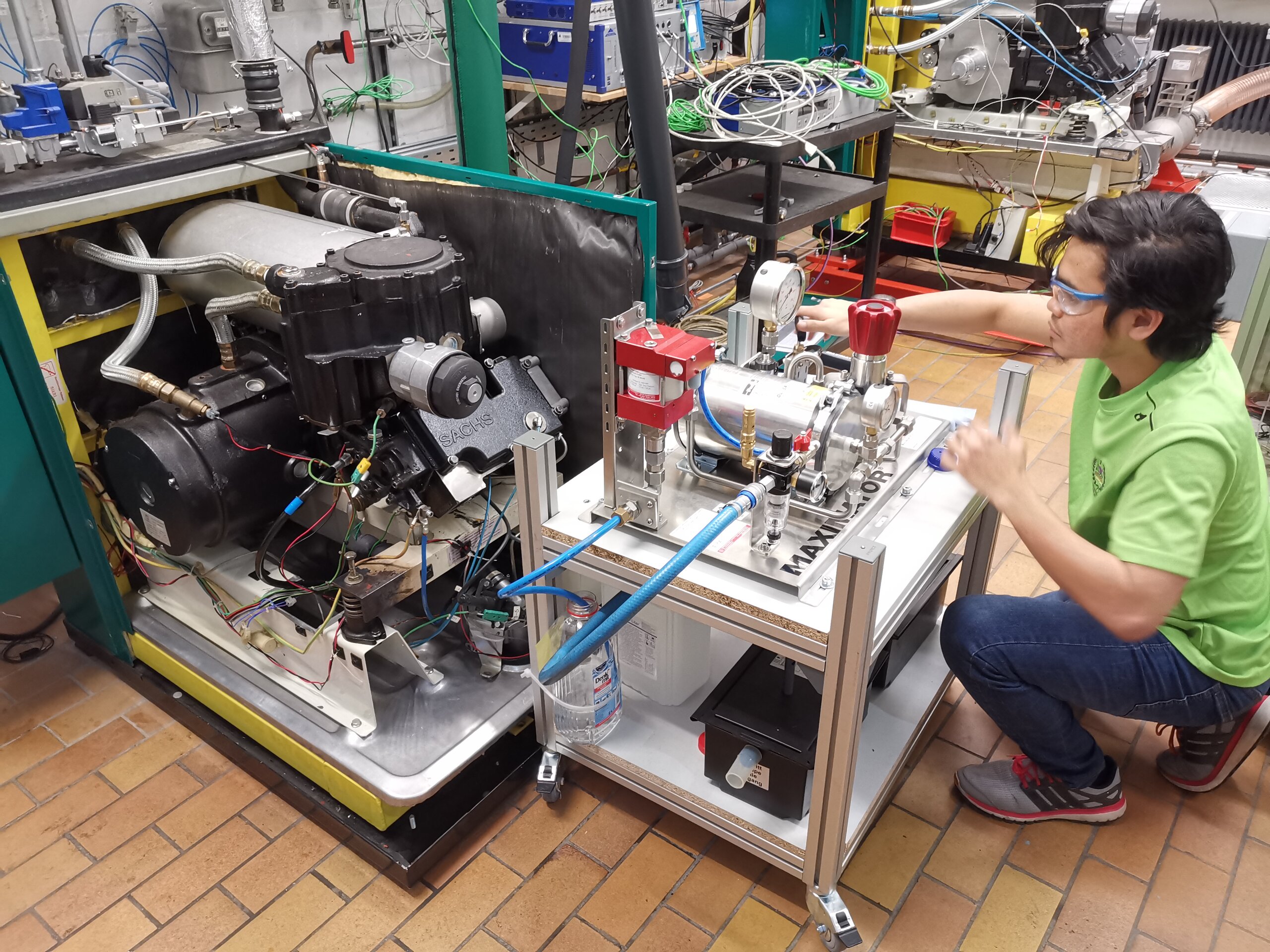
Within the project described, a fully indexed single-cylinder research test bed based on a production CHP engine was built and modified for HCCI operation. Major modifications include:
- Increase in compression ratio from 13.2 to 21.5
- Integration of a variable-speed (4Q) engine brake
- Integration of an 11 kW intake air heater
- Development of a camshaft for operation with exhaust gas retention
- Further details: test bench
The design of the compression ratio, speed and EGR camshaft were carried out using complementary simulation tools. The influence of the intended individual measures on the auto-ignition tendency was fully factorially investigated by means of 1D engine process simulation (AVL Boost) as well as a six-zone combustion model and chemical reaction kinetics. As a result, a target compression ratio of 21.5:1 was implemented by modifying the piston cavity. The realization of the targeted timing (intake, exhaust) was achieved by determining the grinding coordinates using multi-body simulation (AVL Excite).
Current information about the project
The developed test rig is continuously used to investigate the HCCI process as well as alternative processes based on compression ignition.
![[Translate to English:] Entwicklungsmethodik der thermodynamischen Auslegung des Brennverfahrens](/fileadmin/_processed_/9/c/csm_HKA_WE-IKKU_Imagefoto_GenLab_HCCI_02_7e14e2185c.png)
Related publications
- Judith J, Neher D, Kettner M, Klaissle M, Kozarac D: Numerische Untersuchungen zu den Selbstzündbereichen eines erdgasbetriebenen HCCI-Motors. In: SAE Technical Papers, ISSN 0148-7191 (2017), 14 S. (Elektronische Veröffentlichung: http://papers.sae.org/2017-32-0073/)
Project partner
Ministry of Science, Research and the Arts Baden-Württemberg
Funding period
2016 – 2019
Last updated
26.02.2021