HSACI
Hot Surface Assisted Compression Ignition
Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition (HCCI) is a suitable combustion process for achieving high efficiencies and very low NOx emissions. Due to the almost simultaneous auto-ignition of the extremely lean fuel-air mixture in the HCCI process, very high pressure gradients and peak pressures occur, which often only allow operation in the low to medium load range. Furthermore, the strong time dependence of auto-ignition leads to a limitation of the speed range towards higher speeds, which means that overall only comparatively low engine performance can be achieved compared to spark ignition processes.
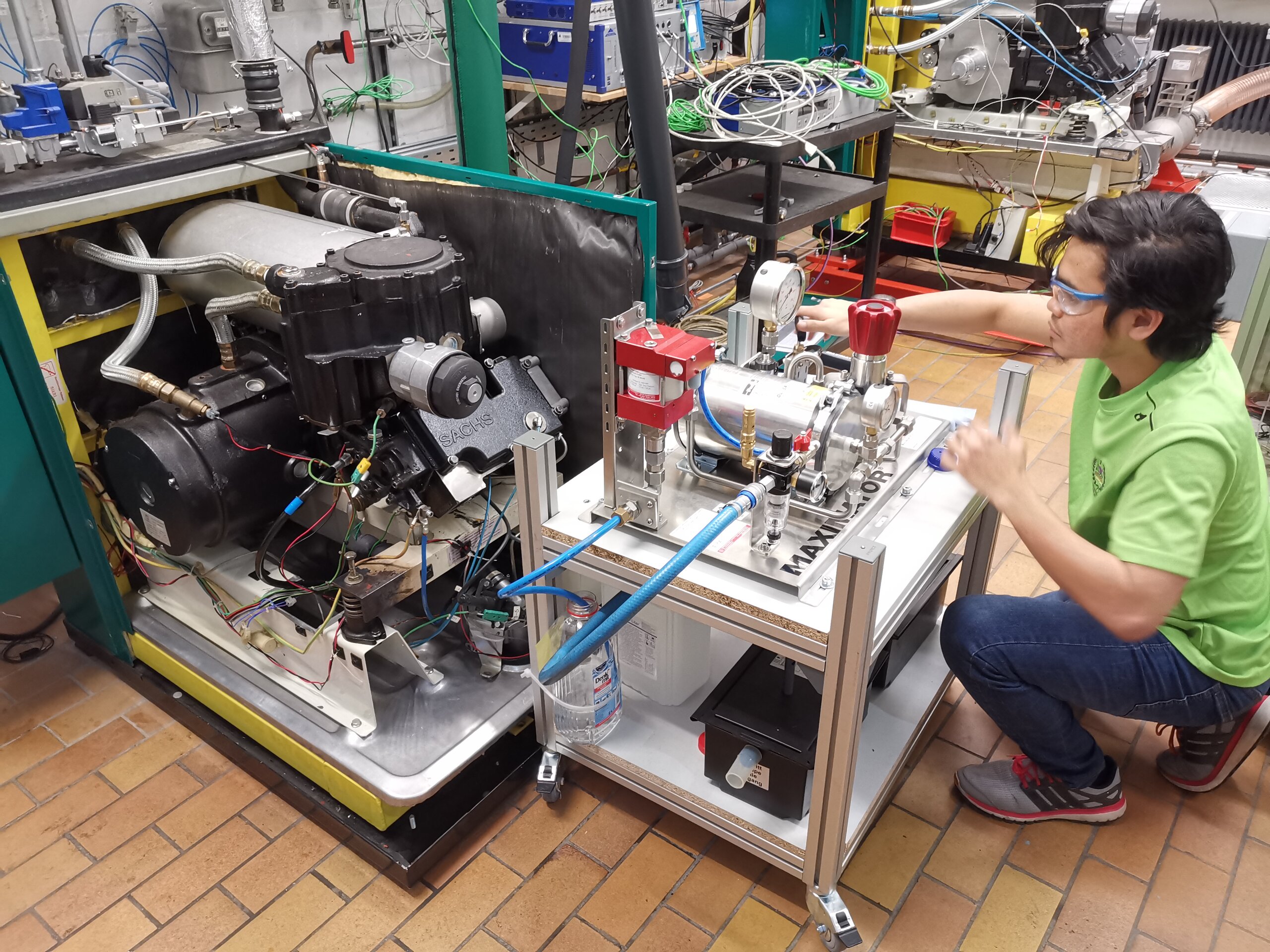
The aim of the project is to develop measures to extend the described operating limits of the HCCI process for a single-cylinder natural gas CHP engine. The measures to be developed are intended to enable monovalent operation of the engine with compression ignition and to exploit the advantage of high efficiency with low NOx emissions in an extended operating range. The basis for extending the HCCI process is a controlled hot surface, which was used in a previous project to develop a combustion process with surface ignition (HSI). Starting from a local surface ignition, the unburned mixture is to be brought to compression ignition by the combined compression of piston motion and initial flame propagation. The resulting combustion process represents a combination of "Hot Surface Ignition - HSI" and "Homogeneous Charge Compression Ignition - HCCI" and is referred to in this context as "Hot Surface Assisted Compression Ignition - HSACI" (see Figure 1). Against the background of future power-to-gas technologies, increased hydrogen contents in the fuel gas-air mixture are further investigated with regard to the influence on (assisted) compression ignition.
![[Translate to English:] 3D-CFD-Ergebnisse (links) und Vergleich der Brennverfahren anhand der Wärmefreisetzung (rechts), aus [1]](/fileadmin/Hochschule_Karlsruhe_HKA/Bilder_WE-IKKU/GenLab/HKA_WE-IKKU_Imagefoto_GenLab_HSACI_01.png)
Current information about the project
In the context of the project, the HSACI process will be investigated both experimentally and numerically. For the experimental investigations, the test rig set up within the HCCI project as well as the ignition element developed in the HSI project will be used. The numerical investigations include 0D basic investigations (Cantera, AVL Fire), 1D engine process simulations (AVL Boost) and 3D combustion simulations (AVL Fire AVL link). In all cases, chemical reaction mechanisms are used to describe combustion.
Students
For students there is a permanent opportunity to work as a research assistant (Hiwi) or in the context of project (PA, R & D) and thesis (Bachelor, Master) on the test bench or in simulation projects. Open topics can be found under student research or by direct contact with the responsible staff member.
Related publications
- [1] Judith J, Holzberger S, Kettner M, Koch T: Assessment of Solver Setup, Mesh Quality and Time-Step for Simulation of Auto-Ignition and Flame Propagation within a Homogeneous Pre-Mixed Variable Volume Combustion Reactor Using 3D-CFD and Detailed Chemical Kinetics. AVL International Simulation Conference (Graz, Austria, 22.-23.10.2019)
Projectpartners
Last updated
26.02.2021